How to Build a Python Internet Speed Test Script (Step-by-Step Guide)
Learn how to measure your internet speed using Python with the speedtest-cli library. This guide includes the complete script, installation steps, and how to run the test to check download, upload, and ping results in real-time

Ever wondered how fast your internet really is? Instead of relying on websites like Speedtest.net, you can write your own Python script to test your connection. With the help of the speedtest-cli library, you can measure download speed, upload speed, and ping directly from the command line.
In this tutorial, we’ll build a Python Internet Speed Test Script step by step, show you how to run it, and even discuss how you can extend it to log results for tracking your internet performance over time.
Requirements
Before starting, make sure you have:
-
Python 3.6+ installed
-
Internet connection
-
A terminal/command prompt
We’ll also install one Python library: speedtest-cli.
Step 1: Install the Required Package
Open your terminal (Command Prompt on Windows, or Terminal on Linux/Mac) and run:
pip install speedtest-cli
This installs the Python library that interacts with Speedtest servers to measure performance.
Step 2: Create the Script
Open your favorite text editor (VS Code, PyCharm, or even Notepad) and create a new file called internet_speed.py.
Paste the following script:
import speedtest
def test_speed():
st = speedtest.Speedtest()
st.get_best_server()
print("Testing Download speed...")
download = st.download() / 1_000_000 # Convert to Mbps
print("Testing Upload speed...")
upload = st.upload() / 1_000_000 # Convert to Mbps
ping = st.results.ping
print("\n--- Internet Speed Test Results ---")
print(f"Download Speed: {download:.2f} Mbps")
print(f"Upload Speed : {upload:.2f} Mbps")
print(f"Ping : {ping:.2f} ms")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_speed()
Step 3: Run the Script
Navigate to the folder where you saved the file and run:
python internet_speed.py
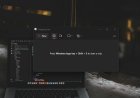
You’ll see output like this:
--- Internet Speed Test Results ---
Download Speed: 52.34 Mbps
Upload Speed : 11.45 Mbps
Ping : 23.67 ms
Understanding the Results
-
Download Speed (Mbps): How fast you can receive data (important for streaming, browsing, downloads).
-
Upload Speed (Mbps): How fast you can send data (important for video calls, uploads, cloud backups).
-
Ping (ms): The delay between your computer and the server (lower is better for gaming and calls).
Bonus: Extend the Script
You can extend this script to:
-
Log results into a CSV file for historical tracking.
-
Schedule it with Task Scheduler (Windows) or cron (Linux/Mac) to run automatically at set times.
-
Send alerts if your speed drops below a certain threshold.
For example, to save results in a CSV:
import speedtest, csv, datetime
def log_speed():
st = speedtest.Speedtest()
st.get_best_server()
download = st.download() / 1_000_000
upload = st.upload() / 1_000_000
ping = st.results.ping
time_now = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
with open("speed_log.csv", "a", newline="") as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow([time_now, f"{download:.2f}", f"{upload:.2f}", f"{ping:.2f}"])
print("Result logged at", time_now)
if __name__ == "__main__":
log_speed()
Conclusion
With just a few lines of Python, you’ve created a powerful internet speed test tool that measures download, upload, and ping directly from your terminal. Unlike online speed test websites, this script is fully customizable — you can log results, schedule tests, or even integrate it into monitoring dashboards.
If you’re learning Python, this is a fun and practical project to improve your coding and networking skills while keeping an eye on your internet provider’s performance.
What's Your Reaction?



























![2024 Social Media Image Sizes for All Networks [CHEATSHEET]](https://blogs.amospeter.co.ke/uploads/images/202406/image_430x256_666ad3fcd2380.jpg)